Introduce EzyFox Bean
Updated at 1699803762000EzyFox Bean Introduction
EzyFox Bean is a library for bean managment and dependency injection. It can manage the both singleton objects and prototype objects.1. Structure of EzyFox Bean
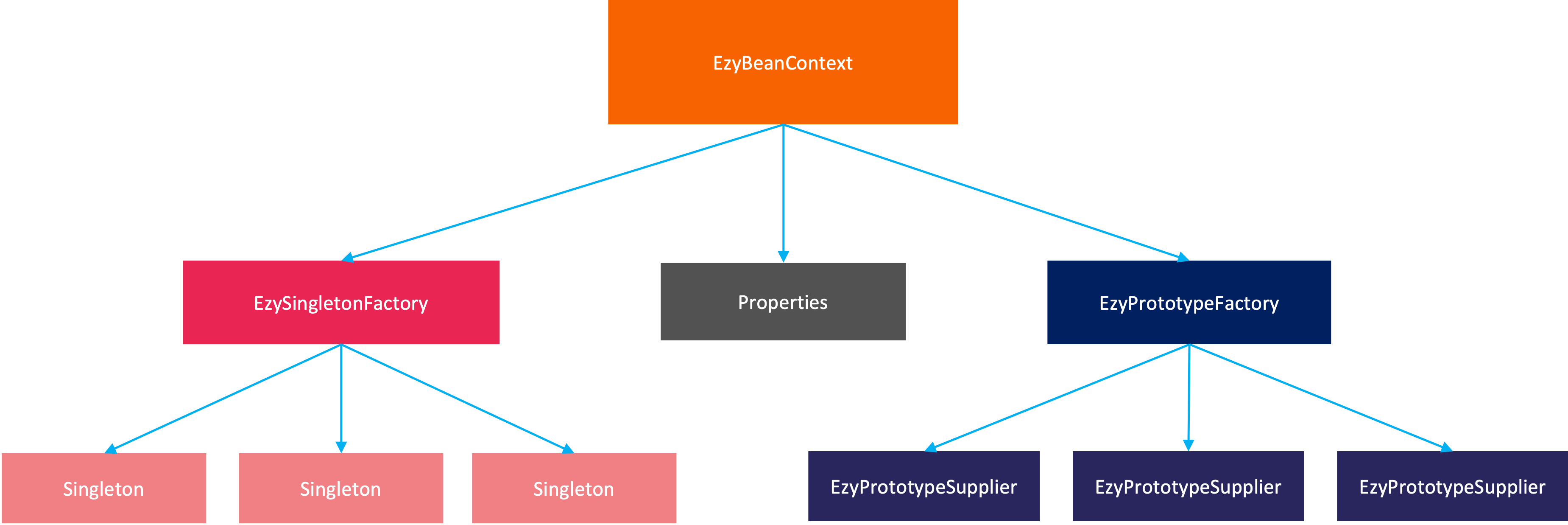
- EzyBeanContext: a composite object, manage all properties, singletons and prototypes
- Properties: EzyBeanContext will keep all properties and inject to singletons and prototypes
- EzySingletonFactory: manage all singletons
- EzyPrototypeFactory: manage all prototypes
EzyFox Bean also has many annotations and you can find out theme here.
2. Install EzyFox Bean
You can add to your dependency like this:
<dependency> <groupId>com.tvd12</groupId> <artifactId>ezyfox-bean</artifactId> <version>1.2.8</version> </dependency>
The latest version can be found in the Maven Central repository.
3. Properties
Currently, EzyFox Bean support .properties and yaml file. By default, it will read files in your classpath:
- application.properties
- application.yaml
- application.yml
Let's say you have a application.properties like this:
book.name_pattern=[a-zA-Z\s]+
book.min_price=1000
You can create a data class and EzyFox Bean will bind the properties to it automatically. Example:
@EzyPropertiesBean(prefix = "book")
public class BookSetting {
@Property("name_pattern")
private String namePattern;
@Property("min_price")
private long minPrice;
}
4. Singleton management
Bean initialization
EzyFox Bean will scan which packages that you provide and by default it will scan com.tvd12.ezyfox.boot package. It find which classes are annotated with @EzySingleton, @EzyConfigurationBefore, @EzyConfiguration, @EzyConfigurationAfter to create singleton objects. Example, you have BookRepository class like bellow, EzyFox Bean will scan and create singleton for it.
@EzySingleton
public class BookRepository {
public void save(Book book) {
System.out.println("saved book: " + book);
}
}
Bean binding
EzyFox Bean support binding vi constructor and @EzyAutoBind annotation, but we recommend you use constructor binding because you will don't need use setter method and make your class is immutable. Example:
@EzySingleton
@AllArgsConstructor
public class BookService {
private final BookSetting bookSetting;
private final BookRepository bookRepository;
public void saveBook(Book book) {
if (!book.getName().matches(bookSetting.getNamePattern())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("invalid book name");
}
bookRepository.save(book);
}
}
5. Prototype management
EzyFox Bean will create a prototype supplier for a class that's annotated by @EzyPrototype annotation, example:
@Setter
@EzyPrototype
public class BookPriceCalculator {
private Book book;
@EzyProperty("book.discount")
private int discount;
public long calculate() {
return book.getPrice() - discount;
}
}
4. Example
Now combine properties, singletons and prototypes we can create a EzyBeanContext and get bean (singleton and prototype) to use:
public final class EzyFoxBeanExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final EzyBeanContext beanContext = EzyBeanContext.builder()
.scan("com.tvd12.ezyfox.example.bean")
.build();
final BookController bookController =
beanContext.getBeanCast(BookController.class);
final Book book = new Book(1L, "EzyFox in action", 2000);
bookController.saveBook(book);
final BookPriceCalculator bookPriceCalculator =
beanContext.getBeanCast(BookPriceCalculator.class);
bookPriceCalculator.setBook(book);
final long bookPrice = bookPriceCalculator.calculate();
System.out.println("book price: " + bookPrice);
}
}

